TCM Theory: Channels and Collaterals
7.The Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang
Circulation and Distribution: The Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang starts from the inner canthus jingming. Ascending to the forehead it joins the Du Meridian at the vertex, where a branch arises running to the temple.
The straight portion of the meridian enters and communicates with the brain from the vertex. It then emerges and bifurcates into two lines, descending along the posterior aspect of the neck. Running downward alongside the medial aspect of the scapula and parallel to the vertebral column, it reaches the lumbar region, where it enters the body cavity via the paravertebral muscle to connect with the kidney and join its pertaining organ, the bladder.
The branch of the lumbar region descends through the gluteus region and ends in the popliteal fossa.
The branch from the posterior aspect of the neck runs straight downward along the medial border of the scapula. Passing through the gluteal region downward along the posterior aspect of the thigh on the lateral side, it meets the preceding branch descending from the lumbar region in the popliteal fossa. From there it descend to the leg and further to the posterior aspect of the external malleolus. Then, running along the tuberosity of the 5th metatarsal bone, it reaches the lateral side of the tip of the little toe Zhiyin, where it links with the Kidney Meridian of Foot-Shaoyin(Fig.2-7)
Connection of Zang-fu organs includes brain, kidney and bladder.
Symptom and indication: This meridian is used for treating the diseases of head, neck, eyes, ears, nose, lumbar diseases and the disease of posterior to lower extremities
8 The Kidney Meridian of Foot-Shaoyin
Circulation and Distribution: The Kidney Meridian of Foot-Shaoyin starts from the inferior aspect of the small toe and runs obliquely towards the sole. Emerging from the lower aspect of the tuberosity of the navicular bone and running behind the medial malleolus, it enters the heel. Then it ascends along the medial side of the leg to the medial side of the popliteal fossa and goes further upward along the postero-medial aspect of the thigh towards the vertebra column, where it enters the kidney, its pertaining organ, and connects with the bladder,
Branch: The straight portion of the meridian reemerges from the kidney. Ascending and passing through the liver and diaphragm, it enters the lung, runs along the throat and terminates at the root of the tongue,
A branch springs from the lung, joins the heart and flows into the chest to link with the Pericardium Meridian of Hand-Jueyin(Fig. 2-8).
Connection of Zang-fu organs includes kidney, bladder, liver, lung and heart.
Symptom and Indication: This meridian is used for treating the diseases of genital organ, throat, lung and mental diseases.
9. The Pericardium Meridian of Hand-Jueyin
Circulation and Distribution, The Pericardium Meridian of Hand-Jueyin originates from the chest. Emerging, it enters its pertaining organ, the pericardium. Then, it descends through the diaphragm to the abdomen, connecting successively with the upper, middle and lower jiao.
A branch Arising from the chest runs inside the chest, emerges from hypochondriac region at a point 3 cun below the anterior axillary fold and ascends to the axilla. Following the medial aspect of the upper arm, it runs downward to the forearm ending in the palm. From there it passes along the middle finger right down to its tip Zhongchong.
Another branch arises from the palm at Laogong, runs along the ring finger to its tip Guanchong and links with the Sanjiao Meridian of Hand-Shaoyang(Fig. 2-9).
Connection of Zang-fu organs includes pericardium, and the Sanjiao.
Symptom and Indication: This meridian is used for treating the diseases of heart, chest, mental disease and the diseases or upper extremities.
10. The Sanjiao Meridian of Hand-Shanyang
Circulation and Distribution: The Sanjiao(Triple Energizer) Meridian of Hand-Shaoyang originates from the tip Guanchong of the ring finger, running upward between the 4th and the metacarpal bones along the dorsal aspect of the wrist to the lateral aspect of the forearm between the radius and ulna. Passing through the olecranon along the lateral aspect of the upper arm, it reaches the shoulder region, where it goes across and passes between the Gallbladder Meridian of Foot-Shaoyang. Winding over to the supraclavicular fossa, it spreads in the chest to connect with the pericardium. It then descends through the diaphragm down to the abdomen, and joins its pertaining organ, the upper, middle and lower jiao.
A branch originates from the chest, running upward, it emerges from the supraclavicular fossa. From there it ascends to the neck, running along the posterior border of the ear, and further to the superior aspect of the ear. Then it turns downward to the cheek and terminates in the infraorbital region.
The auricular branch arises from the retroauricular region and enters the ear. Then it emerges in front of the ear, crosses the previous branch at the cheek and reaches the outer canthus Tongziliao to link with the Gallbladder Meridian of Foot-Shaoyang(Fig. 2-10).
Connection of Zang-fu organs includes pericardium.
Symptom and Indication: This meridian is used for treating the diseases of head, ears, eyes and throat. To treat deafness and tinnitus, Zhongzhu point may be punctured since Sanjian Meridian distributes the ears
11. The Gallbladder Meridian of Foot-Shanyang
Circulation and distribution: The Gallbladder Meridian of Foot-Shaoyang originates from the outer canthus Tongziliao, ascends to the corner of the forehead, then curves downward to the retroauricular region and runs along the side of the neck, down to the supraclavicular fossa.
The retroanricular branch arises from the retroauricular region and enters the ear. It then comes out and passes the preauricular region to the posterior aspect of the outer canthus.
The branch arising from the out canthus runs downward to Daying and meets the Sanjiao Meridian of Hand-Shaoyang in the infraobital region. Then, passing through Jiache, it descends to the neck and enters the supraclavicular fossa where it meets the main meridian. From there it further descends into the chest, passes through the diaphragm to connect with the liver and enters its pertaining organ, the gallbladder. Then it runs inside the hypochondriac region, comes out from the lateral side of the lower abdomen near the femoral artery at the inguinal region. From there it runs superficially along the margin of the public hair and goes traversely into the hip region.
The straight portion of the meridian rune downward from the supraclavicular fossa, passes in front of the axilla along the lateral aspect of the chest and through the free ends of the floating ribs to the hip region where it meets the previous branch. Then it descends along the lateral aspect of the thigh to the lateral side of the knee. Going further downward along the anterior aspect of the fibula all the way to its lower end, it reaches the anterior aspect of the external malleolus. It then follows the dorsum of the foot to the lateral side to the tip of the 4th toe. The branch of the dorsum of the foot springs from Zulinqi runs between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones to the distal portion of the great toe and terminates at its hairy region, where it links with Liver Meridian of Foot.Jueying(Fig. 2.11).
Connection of Zang-fu organs includes gallbladder and liver.
Symptom and Indication: This meridian is used for treating the diseases of the lateral side of head, ears, eyes, throat, the region of chest and Costa and lateral side of lower extremities.
12. The Liver Meridian of Foot-Jueyin
Circulation and Distribution: The Liver Meridian of Foot-Jueyin starts from the dorsal hairy region of the great toe. Running upward along the dorsum of foot, passing through Zhongfeng in front of the medial malleolus, it ascends to an area 8 cuns above the medial malleolus, where it runs across and. behind the Spleen Meridian of Foot-Taiyin. Then it runs further upward to the medial side of the knee along the medial aspect of the thigh to the pubic hairy region, where it curves around the external genitalia and goes up to the abdomen. It then runs upward and curves round the stomach to enter the liver, its pertaining organ, and connect with the gallbladder. From there it continues to ascend, passing through the diaphragm, and branching out in the costal and hypochondriac region. Then it ascends along the posterior aspect of the throat to the nasopharynx and connects with the “eye system.” Running further upward, it emerges from the forehead and meets the Du Channel at the vertex.
The branch which arises from the “eye system” runs downward into the cheek and curves around the inner surface of the lips.
The branch arising from the liver passes through the diaphragm, flows into the lung and links with the Lung Meridian of Hand-Taiyin.(Fig. 2-12)
Connection of Zang-fu organs includes liver, gallbladder, stomach, lung, brain and eyes.
Symptom and Indication: This meridian is used for treating the diseases of genital system, urinary system, the region of head, eye, hypochondria, abdomen and medial side of lower extremities.
As state above twelve regular meridians are the passages of flowing of vita-vapor and blood through which vita-vapor and blood can reach the internal organs and the body surface, and limbs to nourish the whole body and form a circling system. The flowing order is:
From Zhongjiao of the Lung Meridian of Hand-Taiyin to the index finger where it connects with the Large Intestine Meridian of Hand-Yangming.
From the index finger of the Large Intestine Meridian of hand-Yangming to the side of nose where it connects with the Stomach Meridian of Foot-Yangming.
From the side of nose, the Stomach Meridian of Foot-Yangming reaches the big toe to connect with the Spleen Meridian of Foot-Taiyin.
From the big toe to the heart, the Spleen Meridian of Foot-Taiyin goes along and connects with the Heart Meridian of Hand-Shaoyin in the end.
The Heart Meridian of Hand-Shaoyin goes from the heart to the small finger where it connects with the Small Intestine Meridian of Hand-Taiyang.
The Small Intestine Meridian of Hand-Taiyang goes from the small finger to the inner canthus where it connects with the Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang.
The Bladder Meridian of Foot-Taiyang goes from the inner canthus to the small toe where it connects Kidney Meridian of Foot – Shaoyin.
The Kidney Meridian of Foot-Shaoyin goes from the small toe to the chest where it connects with the Pericardium Meridian of Hand-Jueyin.
The Pericardium Meridian of Hand-Jueyin goes from the chest to the ring finger where it connects the Sanjiao Meridian of Hand-Shaoyang.
The Sanjiao Meridian of Hand-Shanyang goes from the ring finger to the outer canthus where it connects the Gallbladder Meridian of Foot-Shaoyang.
The Gallbladder Meridian of Foot-Shaoyang goes from the outer canthus to the big toe where it connects the Liver Meridian of Foot-Jueyin.
The Liver Meridian of Foot-Jueying goes from the big toe to the lung where it connects with the Lung Meridian of Hand-Taiyin. (Fig. 2 – 13)
Du Meridian and Ren Meridian
1. The Du Channel
Circulation and Distribution: The Du Meridian originates from the inside of the lower abdomen. Descending, it emerges at the perineum. Then it ascends 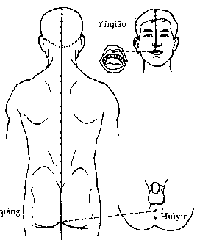 posterior along the interior of the spinal column to Fengfu at the nape, where it enters the brain. It further ascends to the vertex and winds along the forehead to the columella of the nose.
posterior along the interior of the spinal column to Fengfu at the nape, where it enters the brain. It further ascends to the vertex and winds along the forehead to the columella of the nose.
Connection of Zang-fu organs includes brain, spinal cord, liver, kidney and womb.
Symptom and Indication: This meridian is used for treating the mental diseases, neuropathy, the diseases of circulatory system, the diseases of urinary and genital system, lumbar and sacral diseases, the diseases of head, neck and corresponding internal organs. To treat the acute lumbar muscle sprain, Shuigou point may be punctured
2. The Ren Channel
Circulation and Distribution: The Ren Meridian starts from the inside of the lower abdomen and emerges from the perineum. It runs anteriorly to the 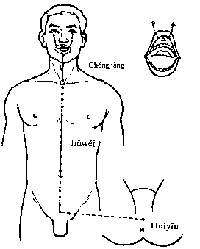 public region and ascends along the interior of the abdomen, passing through Guanyuan and the other points along the front midline to the throat. Running further upward, it curves around the lips, passes through the cheek and enters the infraorbital region. The branch arising from chest region runs downwards into the lung, and links with the lung meridian.
public region and ascends along the interior of the abdomen, passing through Guanyuan and the other points along the front midline to the throat. Running further upward, it curves around the lips, passes through the cheek and enters the infraorbital region. The branch arising from chest region runs downwards into the lung, and links with the lung meridian.
Connection of Zang-fu includes lung, womb, etc.
Symptom and Indication: This meridian is used for treating the diseases of abdomen, chest, neck, head, face and corresponding internal organs,
Twelve meridians, Ren Channel, and Du Channel are the 14 main components of the meridian system.
Please browse the following contents for further study:
OPENING HOURS
| Week Days | 8:00 – 5:00 |
| Saturday | 9:00 – 5:00 |
| Sunday | 11:00 – 4:00 |